MS Windows utility
System requirements
WindowsXP SP3 or Windows7 with USB or Bluetooth connectivity.
Turning it on
Connect the device to the computer or an USB power adapter with a USB cable. The front-side LED continuously glows as the device searches for connection over the USB cable. If the USB connection has been successfully established, the device will communicate via USB, otherwise the connection will be made over Bluetooth The USB channel selection is shown as single LED blinking, Bluetooth channel selection is shown as double LED blinking.
Connecting to the BlueDSO device:
After connecting the device to an USB power supply, the blink of the front-side LED shows which type of communication has been selected.
After starting the BlueDSO utility, the computer automatically tries to connect via the most recently used communication port (COM port). When the connection successfully establishes, the icon in the “Com” field turns green. The icon turns yellow if the recent COM port exists, but it couldn’t find a BlueDSO device on it. It turs red if the recent COM port does not exist on the computer.
If the automatic connection haven’t been successful (e.g. at first time there is no information on recently used ports) and you know the port number, than you can select the port to use in the “Com” field. After that, you can establish connection by clicking the “Connect” button. The icon turns green if the connection was successful.
If the port number is unknown, you can search for it with the “Search BlueDSO” feature, which can be found on the toolbar. The software automatically connects and the icon turns green if any device have been found.
Input voltage dividers
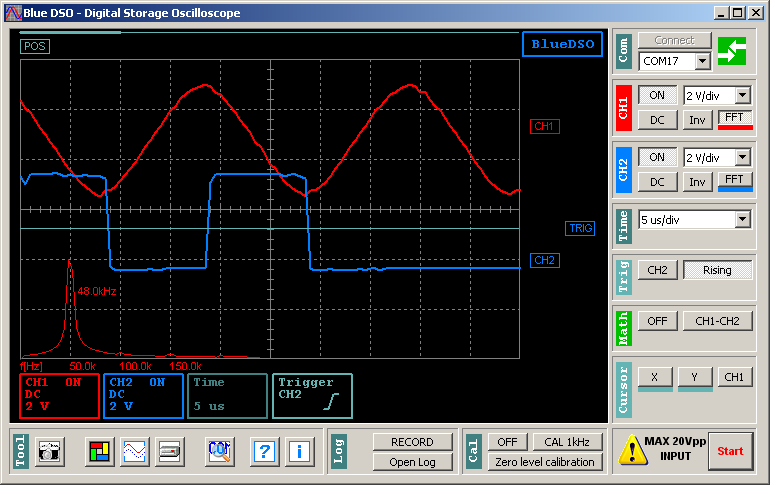
The inputs’ range can be set within the range of 100mV/div – 5V/div in the “CH1-CH2″ field. The maximal voltage connected to the inputs is 20V peak-to-peak. Higher incoming voltage can lead to hardware failure.
The channels’ signal’s visualization can be turned off as needed (ON/OFF). This only turns off the visualization, not the detection, therefore triggering is possible for invisible channels.
The DC component of the measured signal can be detached (AC/DC). The detachment occurs right on the input, before the input voltage divider, which ensures that the measurement unit’s null-point would stay properly calibrated.
The phase of the visualized signal can be inverted (Inv). Phase inversion only affects visualization, the sensors are not affected.
The vertical position of the channels’ signals can be set with the CH1, CH2 elements.
The spectrum of the analysed signal can be visualized by turning the fast Fourier transformation (FTT) on. The frequency is calibrated when showing the FTT. The amplitudes’ relative position carries the important information.
Time base
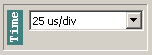
The time base used by the BlueDSO device can be set within the range of 250ns/div – 250 ms/div in the “Time” field. In 5us/div – 250ms/div range the device samples both channels’ signal real-time, so any kind of periodic or transient signal can be observed with the device.
In the 250ns/div – 2,5us/div range the sampling is not real-time, the device does the so-called “Equivalent Time” sampling, therefore in this range only periodic signals’ observation would result in useful information.
The horizontal position of the channels’ signals can be moved with the POS draggable element, so transient signals can be observed beyond the display matices’ limitations.
Trigger
 Setting the trigger source (CH1 – CH2 – Line) and mode (Rising–Falling) is possible on the “Trig” panel. Selecting CH1 or CH2 makes the trigger sensitive for that channel. If the source is set to “Line”, the signal processing takes place without triggering. The “Falling” and ”Rising” options make the trigger sensitive to the edge selected.
Setting the trigger source (CH1 – CH2 – Line) and mode (Rising–Falling) is possible on the “Trig” panel. Selecting CH1 or CH2 makes the trigger sensitive for that channel. If the source is set to “Line”, the signal processing takes place without triggering. The “Falling” and ”Rising” options make the trigger sensitive to the edge selected.
Trigger level can be set with the TRIG draggable element.
Virtual channel
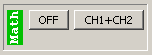 The “Math” virtual channel is the sum or difference of the CH1 and CH2 channels. The available operations are CH1+CH2, CH1-CH2 and CH2-CH1.
The “Math” virtual channel is the sum or difference of the CH1 and CH2 channels. The available operations are CH1+CH2, CH1-CH2 and CH2-CH1.
The vertical position of the “Math” channel can be set with the “MATH” draggable element.
Markers
Both horizontal and vertical markers can be turned on/off and assigned to a channel’s X axis on the “Cursor” panel. With the help of markers you can measure exact time and voltage difference, both of which are shown on the bottom of the black graphing area. The marker lines can be moved to the desired position with their corresponding draggable elements (X1, X2, Y1, Y2).
Calibration wave
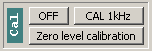
Either a 1kHz or a 10kHz square wave can be connected to the device’s front-side “CAL” output on the “Cal” panel. The amplitude of the square wave is approx. 3.5V.
Data recording
Data capturing can be enabled with the “RECORD” button in the “Log” panel. In this case, the whole data stream registered will be saved. This functionality currently supports from 2,5 ms/div to 250 ms/div time bases. When using it with 2,5 ms/div setting, data sampling occurs every 250 us. Using this functionality with 250 ms/div selected, samping takes place in every 10 ms. The recordable data stream’s duration is only limited by your computer’s free storage, thus it can record several hours if you want. The recorded data stream can be read and analized with the software by clicking on “Open log”.
Toolbar
Save display view: here you can make a snapshot of the graph display in .bmp or .jpg format.
Setting the colours: various items’ colour can be adjusted by clicking the vertical bar on the corresponding panel. The “Restore default colour” button resets all the colour settings.
Graphing mode: the “Vectors/dots” button toggles visualisation to show the result either as a continuous line or a set of dots.
Save settings: here you can save your personal settings, therefore they will be restored on next launch.
Search BlueDSO: here you can search and connect to a BlueDSO device connected to your computer.




 Visit Today : 44
Visit Today : 44 Who's Online : 1
Who's Online : 1